
Reviewed By: Barbara Rexer, DSW, LCSW, LCADC, CCS, ICCS, DRCC
Taking melatonin can help you fall asleep, but is it possible to overdose? If you take too much of any drug, even naturally-occurring substances in the body, they can produce unwanted results. Melatonin is no exception. Here’s what you need to know about the potential of melatonin overdose, and how you can avoid it.
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by your brain’s pineal gland. Its primary job is to regulate sleep cycles, supporting a healthy circadian rhythm. Melatonin levels typically rise during the evening, peak during the night, and lower as it nears morning. You can also find naturally occurring melatonin in some foods, although usually in small amounts. Melatonin supplements are also widely available.
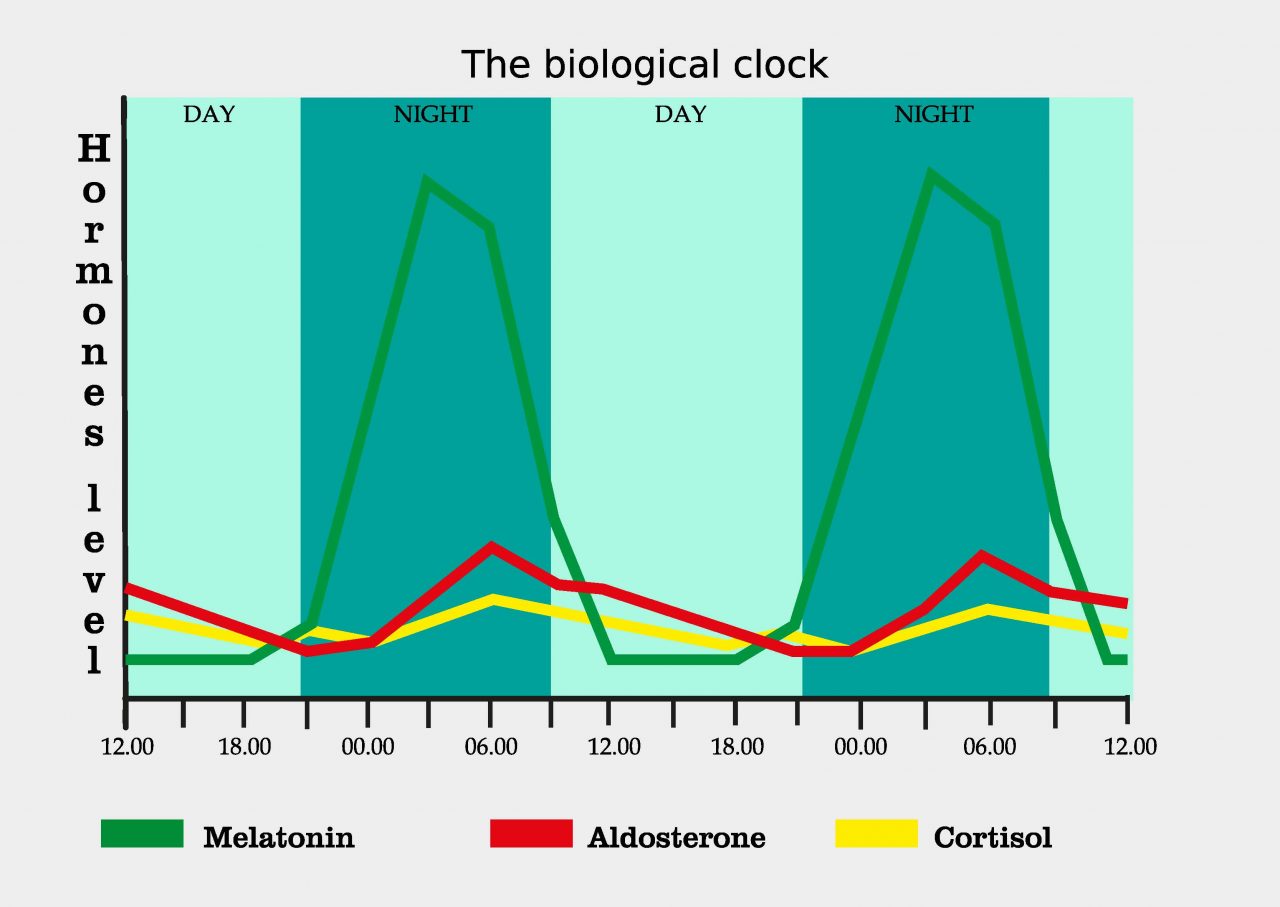
Why People Take Artificial Melatonin
Since melatonin regulates the sleep cycle, individuals who suffer from sleep-related issues, like insomnia, may take artificial melatonin as a supplement. Similarly, travelers may use melatonin to reduce jet lag and adjust to a different time zone. Night shift workers may also take the supplement to make falling asleep during the day or at odd times easier.
When taken before bed, supplements increase the amount of melatonin in the body. This could make falling asleep or staying asleep easier. However, there is limited scientific evidence regarding the effectiveness of melatonin supplements, so it isn’t clear whether people experience the purported benefits or simply a placebo effect.
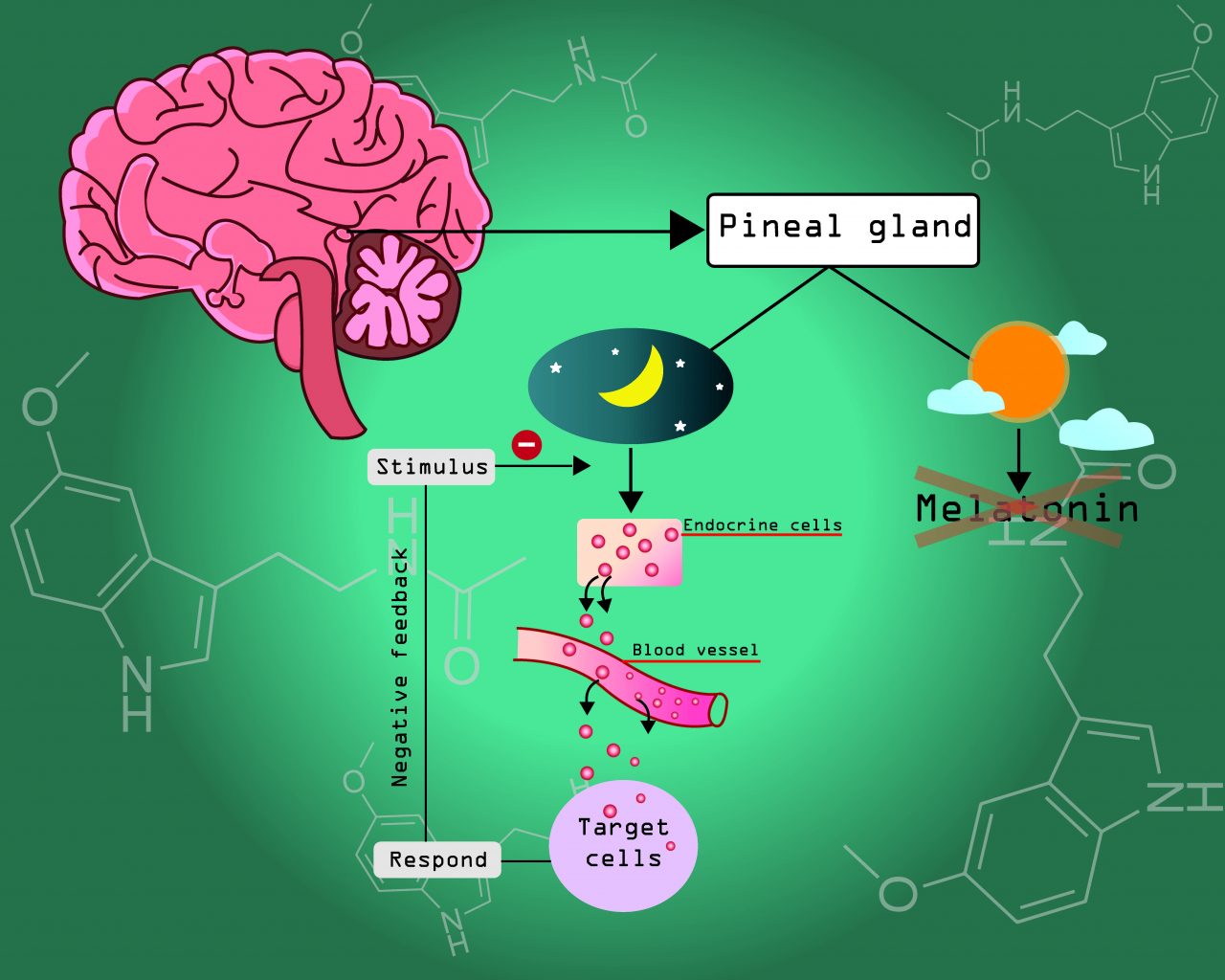
As shown above, outside factors like sunlight can hinder your body’s production of melatonin. Supplements can bypass those factors and help you feel more ready to sleep, even if your environment is less than ideal.
Have questions about addiction?
Call us at 855-430-9426 to speak with a recovery specialist.
Symptoms of Melatonin Overdose
It’s important to note that there isn’t a “safe” dosage of melatonin. Generally, an adult dose is thought to be between 1 and 10 mg. Doses near the 30 mg mark are usually considered to be harmful. However, people’s sensitivity to it can vary, making some more prone to side effects at lower doses than others. Taking too much melatonin for you can lead to unpleasant side effects. These may include:
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Mood changes
- Digestive distress (diarrhea, upset stomach)
- Anxiety
- Joint pain
Young children can experience even more serious side effects, and melatonin overdose occurs more quickly. For example, a dose as small as 1 to 5 mg could cause seizures. It’s important to speak with a doctor before taking supplemental melatonin. The American Academy of Pediatrics offers more information.
Need to talk to someone today?
Call us at 855-430-9426 to speak with a recovery specialist.
Risks of Taking Other Drugs with Melatonin
Taking melatonin in any amount can be dangerous if you are also taking certain other medications. Unfortunately, this includes medications that can also make it difficult to sleep. People who use blood pressure drugs, for example, may have a lower amount of naturally occurring melatonin. However, taking melatonin can cause blood pressure spikes, which could be incredibly dangerous.
On the other end of the spectrum, birth control pills can lead to elevated melatonin production. Taking a supplement could push your concentration into dangerous territory. Individuals using anticoagulants may see an increased risk of bleeding if they also use melatonin. Those on corticosteroids should also avoid the supplement. It also isn’t wise to take melatonin in conjunction with caffeine or alcohol. Both of those substances impact circadian rhythms and natural melatonin production.
Alternatives to Taking Melatonin
If you have trouble sleeping, it is always wise to see a doctor. A doctor can assess your symptoms and determine if a medical condition may be an underlying cause. If that turns out to be the case, your doctor can then identify treatment options that may also allow you to sleep soundly.
If you want a more restful sleep without melatonin supplements, start by establishing a sleep/wake routine. By following the same schedule nightly, you can create a pattern that your body gets used to, increasing the odds that you’ll be sleepy at the right time.
Avoid caffeine, alcohol, exercise and digital devices at least a few hours before bed. All of those things can disrupt your natural melatonin production, so forgoing them as the evening approaches can help. Anxiety can also hamper sleep. Finding natural ways to relieve stress can help.
For some, herbal tea can promote better sleep. Some find consuming them relaxing, and that general sense of calm can make a difference.
Have questions about addiction?Chat with one of our recovery specialists now.

Written By: Sprout Editorial Team
The Sprout Health Group editorial team is passionate about addiction treatment, recovery and mental health issues. Every article is expert-reviewed.